- Home » NPK Fertilizer Guide: Chloride vs Sulfate vs Nitrate Types
NPK Fertilizer Guide: Chloride vs Sulfate vs Nitrate Types
Modern crop production increasingly depends on precise and efficient nutrient management. As a result, NPK fertilizers remain a cornerstone of global agriculture, supplying plants with the three essential macronutrients required for growth, yield, and quality.
At the same time, experienced growers and agronomists recognize that fertilizer performance is not determined by nutrient ratios alone. The chemical form and nutrient source—particularly the type of potassium and nitrogen used—directly affect nutrient availability, soil interaction, and crop tolerance.
As emphasized by professional fertilizer manufacturers such as Terafon Fertilizer, selecting the right NPK formulation is a strategic decision rather than a purely numerical one.
This guide provides a clear and practical explanation of different NPK fertilizer types, focusing on chloride-based, sulfate-based, and nitrate-sulfate formulations, along with guidance on how to choose the most suitable option for specific crops and soil conditions.
Table of Contents
- 1. What Is NPK Fertilizer? Core Principles of Plant Nutrition
- 2. Chloride-Based NPK Fertilizers: Cost-Effective Potassium Sources
- 3. Sulfate-Based NPK Fertilizers: Low-Chloride Solutions for Sensitive Crops
- 4. Nitrate-Sulfate NPK Fertilizers: High-Efficiency Nutrition Systems
- 5. Common Nutrient Sources Used in Modern NPK Fertilizers
- 6. Chloride vs Sulfate vs Nitrate-Sulfate: Key Technical Differences
- 7. How to Choose the Right NPK Fertilizer for Your Crops
- 8. Soil Health, Environmental Impact, and Nutrient Efficiency
- 9. Conclusion: Optimizing NPK Fertilizer Selection

1. What Is NPK Fertilizer? Core Principles of Plant Nutrition
NPK fertilizer refers to compound or blended fertilizers that provide nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in defined proportions. These three nutrients are essential for almost all crops and are universally recognized as the foundation of plant nutrition.
- Nitrogen (N) promotes vegetative growth, chlorophyll production, and protein synthesis
- Phosphorus (P) supports root development, flowering, and energy transfer
Potassium (K) improves water regulation, stress resistance, and overall crop quality
While NPK ratios indicate nutrient quantity, the chemical form of each nutrient determines how efficiently plants can absorb and utilize them, particularly under varying soil and climate conditions.

2. Chloride-Based NPK Fertilizers: Cost-Effective Potassium Sources
Key Characteristics
- High potassium concentration, typically around 60% K₂O equivalent
- Strong cost advantage, making it attractive for large-scale field crops
- Contains chloride, which may accumulate under certain soil or climate conditions
Typical Applications
Chloride-based NPK fertilizers are suitable for chloride-tolerant crops such as cereals, maize, rice, and cotton. They are particularly effective in regions with adequate rainfall or irrigation that helps prevent chloride buildup in the root zone.
3. Sulfate-Based NPK Fertilizers: Low-Chloride Solutions for Sensitive Crops
Core Advantages
- Low or chlorine-free formulation, ideal for chlorine-sensitive crops
- Supplies sulfur, supporting enzyme activity, protein formation, and oil synthesis
Lower salt index, reducing stress on young roots and improving soil compatibility
These fertilizers are widely applied in fruit, vegetable, tobacco, and specialty crop production, where crop quality and nutrient balance are critical.
Many advanced formulations developed by Terafon Fertilizer focus on sulfate-based systems to support high-value crops and long-term soil health.
4. Nitrate-Sulfate NPK Fertilizers: High-Efficiency Nutrition Systems
Nutritional Benefits
- Nitrate nitrogen is immediately available to plant roots
- Improved nutrient synchronization during key growth stages
Minimal chloride content, reducing stress risks
These formulations are commonly used in greenhouse production, fertigation systems, and intensive horticulture, where precise nutrient control directly influences yield and quality.
5. Common Nutrient Sources Used in Modern NPK Fertilizers
Modern NPK fertilizers may include multiple nitrogen and potassium sources to optimize performance:
- Urea for high nitrogen concentration and cost efficiency
- Potassium nitrate (KNO₃) for combined potassium and fast-acting nitrogen
Ammonium-based or calcium-based nitrogen sources to regulate uptake dynamics
Blending different nutrient sources allows manufacturers to tailor fertilizers to specific crops, soils, and application methods.
6. Chloride vs Sulfate vs Nitrate-Sulfate: Key Technical Differences
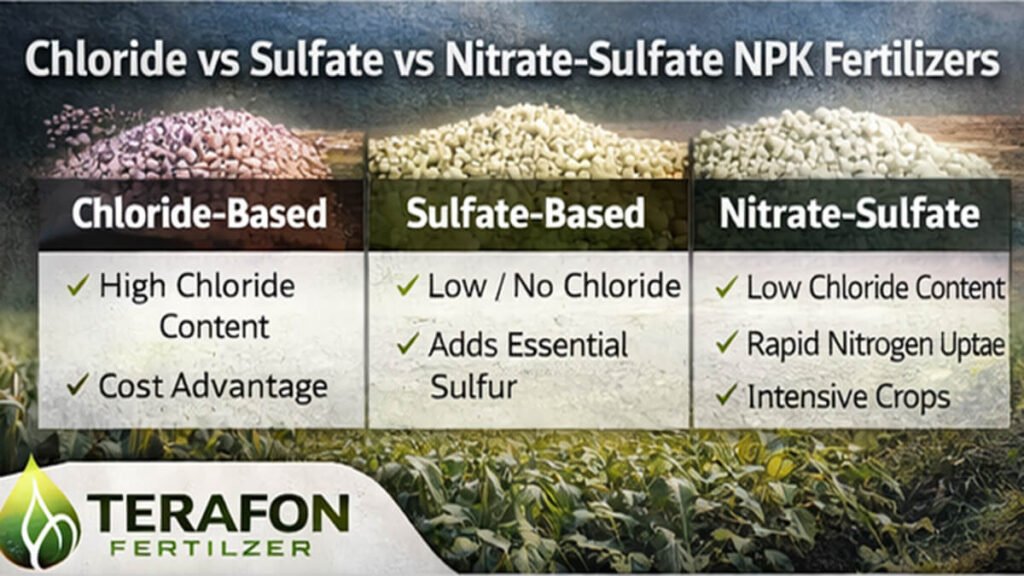
| Parameter | Chloride-Based | Sulfate-Based | Nitrate-Sulfate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloride Content | High | Low / None | Very Low |
| Potassium Source | KCl | K₂SO₄ | Sulfate-based |
| Nitrogen Availability | Variable | Variable | Rapid (nitrate) |
| Sulfur Supply | No | Yes | Yes |
| Best For | Field crops | Quality crops | Precision farming |
7. How to Choose the Right NPK Fertilizer for Your Crops
Choosing the best NPK fertilizer depends on several practical factors:
- Soil test results, including salinity and sulfur levels
- Crop sensitivity to chloride and salt stress
- Application method (basal, top-dressing, or fertigation)
Economic return relative to crop value
Professional fertilizer suppliers such as Terafon Fertilizer often recommend matching nutrient form to crop physiology rather than relying solely on standard NPK ratios.
8. Soil Health, Environmental Impact, and Nutrient Efficiency
Appropriate fertilizer selection supports sustainable agriculture by:
- Reducing chloride accumulation and soil salinity risks
- Improving nutrient use efficiency and crop uptake
Minimizing nutrient losses through leaching or volatilization
Balanced fertilization strategies help protect soil productivity while maintaining high yields.
9. Conclusion: Optimizing NPK Fertilizer Selection

There is no universal NPK fertilizer suitable for all crops and conditions. Chloride-based, sulfate-based, and nitrate-sulfate NPK fertilizers each serve distinct agronomic purposes. Understanding these differences allows growers to make informed decisions that improve yield, quality, and long-term soil health.
By aligning fertilizer formulation with crop requirements and soil conditions—and by working with experienced suppliers like Terafon Fertilizer—producers can move from basic fertilization toward true precision nutrient management.
Get a Catalog & Best Price
Recommended Fertilizers

Urea Fertilizer
View Solutions
NPK Fertilizer
View Solutions
Water Soluble Fertilizer
View Solutions
Fulvic-Acid-Fertilizer
View SolutionsNPK Fertilizer Guide: Chloride, Sulfate & Nitrate Types
Compare chloride-based, sulfate-based, and nitrate-sulfate NPK fertilizers to optimize nutrient efficiency and crop yield. Contact Terafon Fertilizer for expert guidance and tailored solutions to match soil conditions and crop requirements.