Manganese (Mn) is a vital micronutrient that supports photosynthesis, respiration, and enzyme activity. Though required in small amounts, it plays a decisive role in chlorophyll formation, carbohydrate metabolism, and plant stress resistance.
Deficiency quickly limits photosynthetic efficiency and yield, especially in high-pH or organic-rich soils.
1. Key Functions of Manganese
- Photosynthesis: Core element of Photosystem II, enabling water splitting and oxygen release.
- Enzyme Activation: Regulates enzymes for nitrogen and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Antioxidant Defense: Component of Mn-superoxide dismutase, which protects cells from oxidative stress.
Structural Support: Promotes lignin formation and root development.
2. Common Manganese Fertiliser Forms
| Type | Example | Features | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soluble Forms | MnSO₄, Mn-EDTA | Fast correction, suitable for foliar or soil application | Quick fix for visible deficiency |
| Slow-Release Forms | MnO₂, Mn oxides | Gradual supply, long-term soil improvement | Preventive programs |
| Organic Sources | Compost, biofertiliser | Improves soil biology, sustainable | Organic or eco-friendly farming |
3. Application Methods
- Soil Application: Incorporate Mn fertiliser near root zone.
- Foliar Spray: Apply early when new leaves show interveinal chlorosis.
- Seed/Transplant Treatment: Improves early growth in Mn-deficient soils.
Best Practices:
- Avoid over-liming; high pH locks Mn.
- Maintain proper aeration and moisture.
- Combine soil and foliar applications for continuous supply.
4. Manganese Deficiency Symptoms
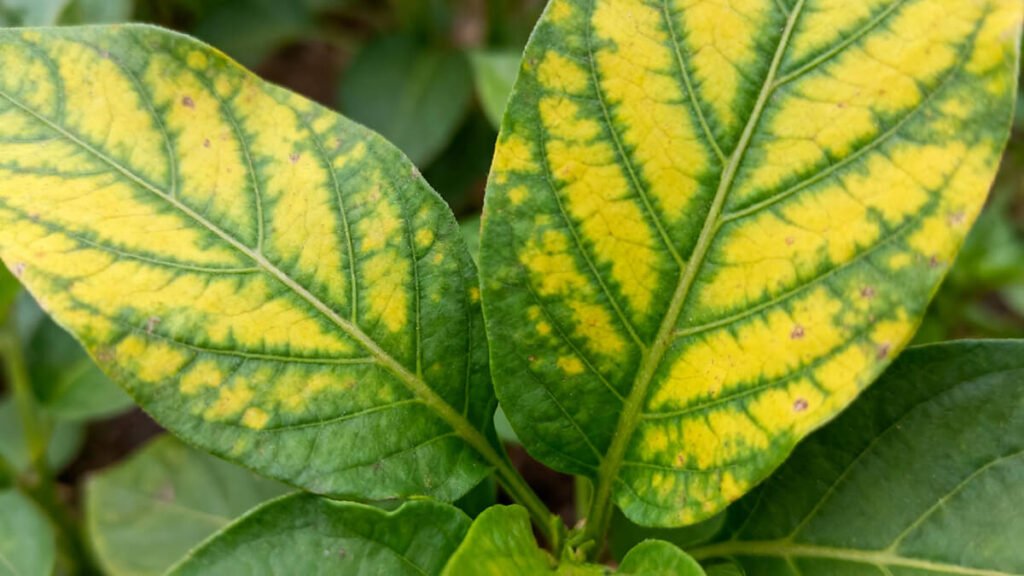

- Inter-veinal yellowing on young leaves
- Brown or grey specks between veins
- Reduced leaf size and weak stems
- Poor photosynthesis and delayed maturity
5. Major Causes of Deficiency
- High soil pH or excess lime
- Sandy, organic-rich, or peat soils
- Water-logging or compaction limiting root uptake
- Imbalance of Ca, Mg, or Fe reducing Mn absorption
6. Correcting Manganese Deficiency

Short-Term Solutions
- Apply foliar MnSO₄ (0.5–1%) or Mn-chelate immediately.
Repeat 10–14 days later if symptoms persist.
Long-Term Strategies
- Maintain soil pH 6.0–6.5.
- Use slow-release Mn for base application.
- Improve root health with organic matter and drainage.
7. Timing and Monitoring
- Pre-plant: Correct low Mn soils before sowing.
- Vegetative Stage: Maintain Mn supply for leaf growth and photosynthesis.
Reproductive Stage: Prevent late-season yellowing and fruit quality loss.
- Soil Test: DTPA-Mn < 5 ppm indicates likely deficiency.
- Tissue Test: Young leaf Mn < 20 ppm = low.
- Visual Signs: Observe new leaves regularly for pale coloration.

8. Preventing Manganese Deficiency
- Balance fertilisation using 4R Nutrient Stewardship (Right Source, Rate, Time, Place).
- Avoid over-liming or heavy irrigation in susceptible soils.
- Use Mn-enriched compost or foliar boosters during rapid growth.
- Rotate deep-root crops to access subsoil Mn.
9. Modern Manganese Management Tools
- Fertiliser management software: Predict Mn demand by crop stage.
- Soil sensors & drones: Detect early deficiency zones.
- GPS precision spraying: Optimise Mn distribution and save costs.
Decision-support systems: Integrate pH, soil data, and weather for smart Mn scheduling.
Table of Contents
Recommended Fertilizers

Urea Fertilizer
View Solutions
NPK Fertilizer
View Solutions
Water Soluble Fertilizer
View Solutions
Fulvic-Acid-Fertilizer
View SolutionsMagnesium Fertilizers: Photosynthesis and Plant Vitality
Magnesium fertilizers support chlorophyll formation, enhance photosynthesis, and improve overall plant growth, while optimized formulations maintain soil nutrient balance and long-term fertility. Terafon Fertilizer provides reliable solutions for efficient and sustainable farming.