- Home » How to Choose the Right Fertilizer for Your Crops
How to Choose the Right Fertilizer for Your Crops

Choosing the right fertilizer for your crops is not about applying more nutrients—it is about precision, balance, and long-term soil sustainability. A well-designed fertilization program improves crop yield, enhances quality, optimizes nutrient use efficiency, and protects soil health over multiple growing seasons.
As a professional nutrient solution provider, Terafon Fertilizer emphasizes science-based fertilizer selection that aligns crop nutrition with soil conditions and modern agricultural practices. This guide explains how to choose the most suitable fertilizer for your crops using proven agronomic principles.
Table of Contents
- 1. What Are Water-Soluble Fertilizers?
- 2. Classification of Water-Soluble Fertilizer Types
- 3. Key Characteristics of Different Water-Soluble Fertilizer Types
- 4. Advantages of Using Water-Soluble Fertilizers
- 5. How to Choose the Right Water-Soluble Fertilizer
- 6. Application Methods and Best Practices
- 7. Future Trends in the Water-Soluble Fertilizer Market
- 8. Conclusion
1. Why Choosing the Right Fertilizer Matters
Correct fertilizer selection is fundamental to profitable and sustainable crop production. When fertilizer types or nutrient ratios do not match soil conditions or crop demand, growers may encounter:
- Excessive vegetative growth with reduced fruit or grain yield
- Low nutrient use efficiency and increased fertilizer losses
- Soil salinity accumulation or pH imbalance
Environmental risks caused by nitrogen and phosphorus leaching
In contrast, fertilizer programs designed around soil analysis and crop growth stages deliver more stable yields, improved crop quality, and lower long-term input costs.
2. Understanding Crop Nutrient Requirements
Essential Nutrients for Crop Growth
All crops require a complete range of nutrients, which are generally divided into:
- Macronutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K)
- Secondary nutrients: Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), Sulfur (S)
- Micronutrients: Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), Boron (B), Manganese (Mn), Copper (Cu), Molybdenum (Mo)
Nitrogen drives leaf growth and photosynthesis, phosphorus supports root development and energy transfer, while potassium improves stress tolerance, nutrient transport, and crop quality. Long-term deficiencies in any of these elements can significantly limit yield potential.
3. Fertilizer Types and Their Functional Differences
Organic Fertilizers vs. Chemical Fertilizers
- Organic fertilizers improve soil structure, increase organic matter content, and enhance microbial activity, making them ideal for building long-term soil fertility
Chemical fertilizers provide fast-acting, precisely formulated nutrients that meet immediate crop demand
Modern crop nutrition strategies increasingly combine organic and mineral fertilizers to achieve both rapid nutrient availability and sustained soil productivity.
Single-Nutrient vs. Compound Fertilizers
- Single-nutrient fertilizers are effective for correcting specific nutrient deficiencies
Compound and NPK fertilizers supply balanced nutrition and are commonly used for base fertilization in field crops, vegetables, and orchards
Selecting the correct NPK formulation reduces unnecessary applications and improves nutrient efficiency.
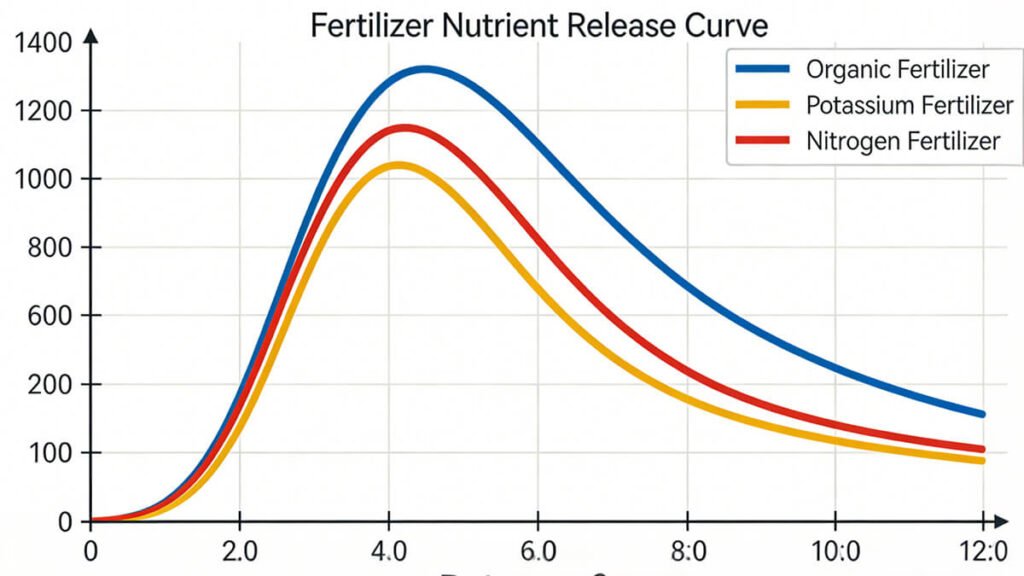
Fast-Release, Slow-Release, and Controlled-Release Fertilizers
- Fast-release fertilizers act quickly but may result in nutrient losses if mismanaged
Slow-release and controlled-release fertilizers provide gradual nutrient availability, aligning with crop uptake patterns
These products are especially valuable for fruit trees, commercial crops, and large-scale farming operations where consistent nutrient supply is critical.
4. The Role of Soil Testing in Fertilizer Selection
Soil testing is the cornerstone of professional fertilizer management. A comprehensive soil analysis reveals:
- Soil pH and buffering capacity
- Existing levels of N, P, and K
Secondary and micronutrient status
With accurate soil data, fertilizer programs can be tailored to actual field conditions rather than assumptions. Many advanced nutrient solutions developed by Terafon Fertilizer are designed to work in combination with soil testing results, enabling precise nutrient matching and improved fertilizer return on investment.
5. Matching Fertilizers to Different Crop Types
Fertilizers for Grain and Cereal Crops
Cereal crops such as maize, wheat, and rice have high nitrogen demand, particularly during early vegetative growth. Balanced phosphorus and potassium fertilization improves root development, lodging resistance, and grain filling efficiency.
Fertilizer Programs for Vegetables and Cash Crops
Vegetables typically have short growth cycles and intensive nutrient requirements:
- Leafy vegetables respond strongly to nitrogen fertilization
- Fruiting vegetables require higher potassium levels to improve fruit size, color, and shelf life
Root and tuber crops benefit from phosphorus-rich fertilizers during early development
Water-soluble fertilizers and fertigation systems can further enhance nutrient uptake efficiency in intensive vegetable production.
Fertilization Strategies for Fruit Trees and Perennial Crops
Fruit trees require a long-term nutrient management approach. Base fertilization using organic matter and slow-release fertilizers builds soil reserves, while targeted nutrient applications during flowering and fruit development support yield stability and quality improvement.
6. Optimizing Nutrient Ratios and Application Methods
Understanding N-P-K Ratios
The N-P-K values on fertilizer labels represent nutrient percentages, not application strength. Selecting the right ratio depends on crop type, soil fertility status, and growth stage rather than choosing the highest nutrient content.
Fertilizer Application Techniques
- Base fertilization establishes nutrient foundations
- Split applications improve nutrient uptake and reduce losses
Fertigation and foliar feeding complement soil fertilization and improve efficiency
A well-planned application strategy is as important as fertilizer selection itself.
7. Common Fertilization Mistakes and Expert Tips
- Selecting fertilizers based only on price
- Relying on a single fertilizer type for multiple seasons
- Neglecting micronutrient deficiencies
Applying fertilizers under unsuitable soil moisture or weather conditions
Professional nutrient management follows the 4R principle: the right fertilizer source, right rate, right time, and right placement.

8. Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Fertilizer Strategy
Choosing the right fertilizer is not a one-time decision but a continuous optimization process. By integrating soil testing, crop nutrient demand, and scientifically formulated fertilizer products, growers can achieve consistent yields, improved nutrient efficiency, and healthier soils.
With a comprehensive product portfolio and agronomic expertise, Terafon Fertilizer supports growers worldwide in developing reliable, crop-specific fertilizer strategies that balance productivity and sustainability.
Recommended Fertilizers

Liquid-Seaweed-Extracts
View Solutions
Macronutrient-Soluble-fertilizer
View Solutions
Micronutrient-Soluble-fertilizer
View Solutions
Functional-Soluble-fertilizer
View SolutionsChoose the Right Fertilizer for Your Crops
Learn how to select the right fertilizer based on soil conditions and crop needs to improve nutrient efficiency and yield. Contact Terafon Fertilizer for professional support and tailored solutions.